
Diet & Cancer
Diet & Cancer
Nutrition plays an important role in cancer prevention. Eating a healthy, balanced diet provides you with macro and micro-nutrients that your body needs & help you keep a healthy body weight. Keeping a healthy weight is important, because obesity is the second biggest preventable cause of cancer after smoking.
Diet can also directly affect cancer risk. Some foods, such as processed and red meat and salt-preserved foods, can increase the risk of developing cancer. While others, such as fruits, vegetables and foods high in fiber can reduce the risk of cancer.
Numerous studies have linked nutritional factors with a risk for developing several types of cancer. The cancers most strongly associated with nutritional factors include cancer of the breast, prostate, colon and rectum, oral cavity, lung, endometrium, and cervix.
Living with Cancer
1. Be as lean as possible without being underweight
Research shows that being overweight or obese increases the risk of cancer. More than half of us are overweight or obese. This put us at increased risk for breast, colorectal, esophageal, gall bladder, liver, kidney, pancreatic and uterine cancer. Maintaining healthy weight reduces the risk for cancer and all diseases. Loosing few kilos if you are overweight or obese will have positive effect on your overall health.
A healthy body weight will be different for everyone.
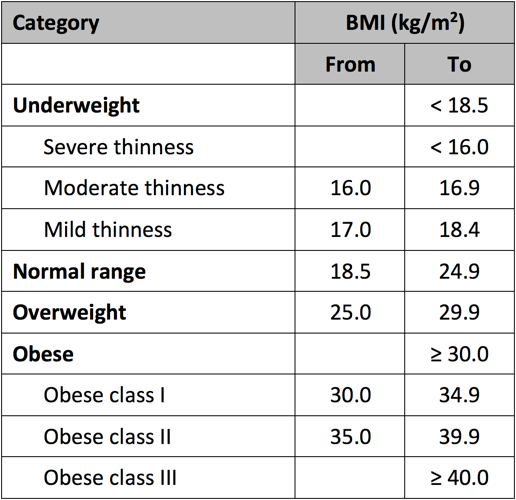
Body mass index (BMI) is a tool used to help decide a person is under weight or over weight. BMI is calculated by dividing the weight (in kilograms) by the height (measured in meters squared). The category of BMI is shown below:
Waist circumference (WC) is another indicator of health risk associated with excess abdominal fat. In general, the risk of developing health problems, including cancer, increases as WC increases above 102cm (40 inches) in men and 88cms (35 inches) in women.
Healthy body weight and cancer
Eating a healthy diet – lots of vegetables and fruits, lots of fiber and little fat and sugar will help you keep a healthy body weight. Research shows that maintaining a healthy body weight reduced your risk of developing cancer. Eat a healthy diet, with an emphasis on plant food
Tips to maintain a healthy weight:
Healthy eating doesn’t have to be complicated, expensive or time-consuming. It’s a habit you get used to, and every day its getting easier. The important thing is to get started now.
- Eat regular meals. Skipping a meal - especially breakfast – can lead to over eating throughout the day. And when you are hungry it’s hard to make healthy choices.
- Fill half your plate with fruits and vegetables, quarter of the plate with whole grains and the other quarter with proteins (fish, chicken, beans and nuts).
- Cut back on portion size. If your portions are a reasonable size, it will be easier for you to eat what you want but still stay healthy.
- Serve everything you eat in a dish – especially snacks. You’ll be much less likely to overeat if you’re not eating out of the box or bag.
- Make changes gradually. For example, if you try to switch from full fat milk to skim, you may give up because you don’t like the taste. Try switching first to low fat, then skim, and you may be more successful.
- Try to plan your meals for the whole week. Last-minute choices are often unhealthy ones.
- Don’t go grocery shopping on an empty stomach. You’ll make better choices if you’re not hungry.
- Don’t eat while watching TV.
- Choose wisely when you eat in restaurants – skip the fries and sugary drinks, and ask for dressings on the side.
- Slow down and enjoy every bite. It actually takes 20 minutes for your brain to get the message that your stomach is full.
- Read food labels to become more aware of portion sizes and calories. Be aware that "low-fat" or "non-fat" does not necessarily mean "low-calorie."
FAT
Fat intake is necessary for everybody which adds taste and texture to the food and makes you full longer. Furthermore, fat in essential for some vitamins absorption and biological function.
Fat requirement
According To AICR, it is recommended to get 20% to 35% of the total calories from fat each day.
For women: 45 – 75 grams of fat a day (using an average of 2000 kcal/day)
For men: 60 – 105 grams of fat a day (using an average of 2500 kcal/ day)
Note: This is an estimated requirement, however the precise requirement depends on your age, activity level and other factors.
Fat sources and types
Fat can be divided into healthy and unhealthy fats, but even the healthy fats should be taken in moderation
Healthy fats (unsaturated fat)
Healthy fat can include the naturally present fat in the avocados, nuts, and seeds, non-hydrogenated soft margarines. Oils like olive oil, canola oil, sunflower oil. Omega – 3 is also a very healthy fat found in oily fish such as salmon, herring, and mackerel.
Note: the healthy diet can include 2 to 3 Tbsp. (30 to 40ml) of fat per day.
Fat to be consumed in limited amounts (saturated fats)
Saturated fat is the fat found in animal food such as meat, poultry, butter and cheese. Also, it can be found in tropical oils like coconut, palm and kernel oils.
Fat to be avoided (Trans fats)
Trans fats are found in foods that are prepared with partially hydrogenated fats like, potato chips, crackers, deep fried fast foods and margarines.
Fat and cancer
Consuming fat rich diet can increase the risk of cancer by gaining weight. Several studies have shown that consuming a lot of animal fat can increase the risk of breast cancer for women after menopause. On the other hand, consuming fish oil (omega 3 fat) can decrease the risk.
Tips to cut down unhealthy fats
- Choose lean cuts and trim off visible fat. Remove skin from poultry and reduce red meat intake.
- Grill, bake or steam instead of frying to reduce the amount of fat consumed.
- Always choose food that is “low fat” dairy products.
- Use less dressing or low-fat dressing on salads.
- Limit how often you eat processed foods.
- Measure oil for cooking with tablespoon rather than pouring of straight from the bottle.
Tips to increase healthy fat intake
- Consume oily fish more often (like salmon and sardines) which contains lots of omega-3 fat.
- Cook with healthy oils like canola oil for frying, sunflower or olive oil.
- Mash potatoes with olive oil and garlic instead of butter.
- Make your own salad dressing with olive oil instead of mayonnaise.
2. Eat a variety of vegetables, fruits, whole grain & legumes such as beans
It is recommended to consume these foods due to their antioxidants and high fiber content which is required for the GI health.
What is a dietary fiber
Dietary fiber is a type of carbohydrate that cannot be digested by our bodies' enzymes. Fiber is grouped by its physical properties to soluble fiber which dissolve in water forming gel that slows down digestion and insoluble fiber which does not dissolve in water; it is the bulky fiber that helps to prevent constipation.
Benefits of fiber
- Prevent heart disease by helping lower cholesterol level
- Reduce digestive problems by help preventing constipation and hemorrhoids and improve diarrhea
- Prevent weight gain A high-fiber eating plan is lower in calories and tends to make you feel full faster and longer
- Help lower blood sugar levels and possibly aid insulin sensitivity
- Protect the lining of the colon and prevent development of cancerous cells
- Serve as “prebiotics” that may protect the colon from cancer
Recommended daily amount
The recommended daily amount of fiber is 25 grams for women and 38 grams for men.
Sources of fiber


Fiber and cancer risk
Research shows that vegetables and fruits probably protect against a range of cancers, including mouth, pharynx, larynx, esophagus and lung
Fiber help to speed up ‘gut transit time’ - how long it takes food to move through the digestive system so decrease the contact time between the food and GIT, also help people maintain a healthy weight because they are low in calories.
Tips to increase fiber intake
- Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables
- Read the nutrition labels (at least 4 grams of fiber per serving)
- Choose whole grain than refined white flour
- Eat a baked potato with skin on instead of mashed potatoes
- Bake with whole grain flour
- Choose oatmeal more often
- Go for whole grain breakfast cereals
Benefits of dietary fiber
- Excellent source of vitamins, minerals and anti-oxidant
- High in fiber which give fullness
- Low in fat and calories
Fruits, vegetables and cancer
Research shows that vegetables and fruits probably protect against a range of cancers, including mouth, pharynx, larynx, esophagus and lung. As well as containing vitamins and minerals, which help keep the body healthy and strengthen the immune system, they are also good sources of phytochemicals (biologically active compounds that can help protect cells in the body from damage that can lead to cancer)
Recommended amount of fruits and vegetables per day
Filling at least half your plate with fruits and veggies in order to make it to the recommended which is 5-7 servings per day
Tips to increase Fruits and vegetables intake
- Try pre-cut packages of fruit (such as melon or pineapple chunks) for a healthy snack
- Buy fruits that are dried, frozen, canned & fresh
- Mix sliced fruit or frozen berries with yogurt or cereal
- Add apple chunks, pineapple, grapes, or raisins to salad
- Make fruit smoothies
- Add dried or fresh fruit to oatmeal, pancakes, and waffles
- Eat seasonally
- Add minced vegetables to scrambled eggs
- Add greens to breakfast smoothies
- Keep dried fruit with you for a fast and easy to go snack
- Substitute soda drinks with 100% fruit juice
- Enhance vegetables with a healthy dip such as hummus, salsa and creamy avocado
- Make healthy chips. You can bake or roast potatoes or even greens for a crunchy snack.
3. Avoid sugary drinks. Limit consumption of caloric-dense food
Sugar
Sugars are carbohydrates that provide energy for the body. The most common sugar in the body is glucose which your brain, major organs and muscles need to function properly.
Is sugar good or bad
Added sugars (sucrose and high fructose corn syrup) that is added to foods during processing, cooking or at the table is high in calories with NO essential nutrients, so it considered bad sugar.
Foods containing natural sugar, like fruit and unsweetened milk and yogurt, do provide nutritional value and are not linked to excess weight, in part because they are more filling and less likely to be eaten to excess.
Recommended daily intake
The World Health Organization recommends that both adults and children reduce the intake of free sugars to less than 10% of total energy intake. A reduction to below 5% of total energy intake brings additional health benefits
Sources of sugar
Natural sugar: found naturally in foods such as fruit (fructose) and milk (lactose)
Added sugar candy, cookies, pastries, doughnuts, dairy desserts, sugar sweetened drinks, soft drinks, sport drinks, energy drinks and juice drinks
Sugar and cancer risk
Does sugar feed cancer? This is one of our most frequently asked questions.
There is no strong evidence that directly links sugar to increased cancer risk, yet there is an indirect link.
All cells in our body — including cancer cells — need sugar (glucose) from our bloodstream for fuel. We get that blood sugar from foods containing carbohydrates, including vegetables, fruits, whole grains and low-fat dairy sources. Some glucose is produced within our bodies from protein.
But eating a lot of high-sugar foods may mean more calories than you need, which leads to excess weight and body fat. It is excess body fat that increases risk of many mcommon cancers. That is why AICR recommends eating a diet rich in nutritious and filling foods, such as whole grains, vegetables, fruit and beans and replacing sugary beverages with low- or no-calorie drinks
Tips to cut down on sugar
- Check nutrition labels to help you avoid foods high in added sugar
- Drink water or unsweetened fruit juices
- Gradually reduce the amount of sugar you take in your coffee or tea
- Have a piece of fruit when you are craving something sweet
- Choose whole grain breakfast cereals that are not coated with sugar/honey
- Have a slice of melon or fresh berries with a low fat yogurt instead of cookies

4. Limit consumption of salty food and food processed with salt
What is Salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl)
Health outcomes of consuming too much salt
Eating too much salt is claimed to raise blood pressure, thereby increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Recommendation for salt intake
Daily intake of salt should be less than 2,400 milligrams equivalent to 1 teaspoon of salt/day
Salt and cancer
Studies have shown that high salt intake (table salt – salt-preserved food) can damage the lining of the stomach which increase the chance of developing stomach cancer.
Tips to cut down on salt
- Check nutrition labels to help you avoid foods high in salt
- Choose foods that are labeled as sodium free- low sodium- reduced sodium or unsalted
- Remove salt shaker from the table
- Use less salt while cooking
- Remove salt from recipes whenever possible & substitute it with herbs
- Reduce intake of preserved food
- Buy unsalted nuts and lower sodium crackers
5. Limit consumption of red meats and avoid processed meat
Importance of protein
Everyone, and certainly those who have been diagnosed with cancer, must consume adequate calories and appropriate amounts of protein to maintain healthy immune system. Protein is important for your body to avoid infection and help in quick recovery.
Foods high in protein

Protein requirement
Most healthy adults need between 45 and 60 grams of complete protein per day, which should account for 10 to 35 percent of their daily caloric intake. However, this requirement depends on the person’s medical and physical condition however, cancer patient needs high protein.
Red processed meat and cancer
Red meat refers to beef, lamb, veal and goat. Eating more than 0.5 kg (cooked) of red meat per week is associated with increased risk of colorectal cancer. However, moderate intake—less than 18 ounces per week—does not increase the risk.
Processes meat is referred to meats that are preserved by smoking, curing or salting or by the addition of preservatives such as bacon, salami, hot dogs and sausages. Many studies have showed that eating 50 grams of processed meat every day can increased the risk of colorectal cancer by 18% (cancer.org) which is equivalent to about 4 strips of bacon or 1 hot dog.
Tips to eat less meat but high protein diet
- Choose the leanest meat and trim any visible fat before cooking
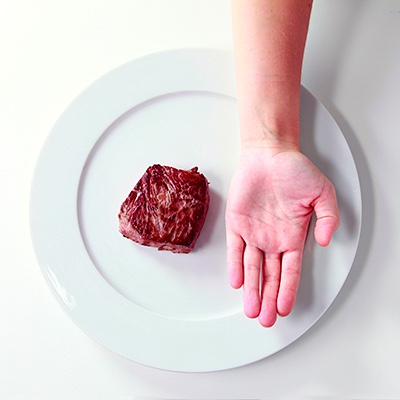
- Limit the amount of red meat you eat to 3 savings per week. The serving is 90 grams (3 ounces)-which is similar to the palm of the hand.
- Choose white meats instead of red meats – like chicken breasts and fish- more often.
- Eat more alternatives, like replacing the meats with beans and legumes.
- Make at least one a week meat-less (meatless Monday).
- Avoid eating processed meat

High protein meatless meals and snacks

veggie wrap with hummus on whole grain bread for lunch

Cashew Noodles with Broccoli and Tofu

Black Bean Salad









